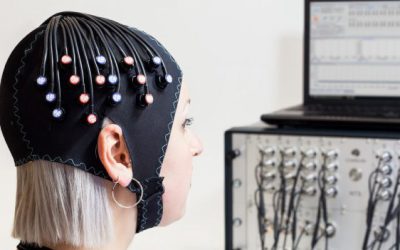
The galvanic skin response (GSR) has always generated great interest in Neuromarketing experts, as it is able to provide key information on people’s emotional involvement (emotional arousal).
Other names commonly used to refer to the galvanic response of the skin (GSR) are: electrodermal activity (EDA) and skin conductance (SC).
In general, GSR is defined as the property of the human body that generates continuous variation in the electrical characteristics of the skin.
What is the association between the galvanic skin response (GSR) and emotions? [Neuromarketing]
When we are very emotionally involved and we are therefore in a state of emotional arousal, our sympathetic nervous system (part of the autonomic nervous system) increases the activity of the sweat glands.
This increase in activity in the sweat glands in turn generates an increase in skin conductance. For this reason, skin conductance is an indirect measure of emotional arousal.

Images used for the study of emotions in a research that involved the use of GSR sensors
Can we discriminate emotions through the study of skin conductance? [Neuromarketing]
Absolutely yes, but an important distinction must be made: GSR can only help the expert to discriminate high arousal emotions from low arousal emotions.
The investigation of the GSR, on the other hand, cannot in any way help to identify differences between positive emotions (positive valence) and negative emotions (negative valence).
GSR therefore plays a crucial role in Neuromarketing if the goal is to monitor the intensity of emotions (arousal) and not the direction (valence).
How is the Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) recorded? [Neuromarketing]
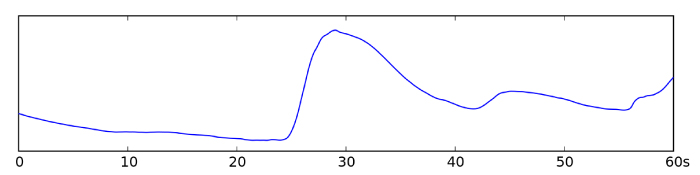
GSR Signal
The GSR signal, represented in the figure above, is very simple to record as it is sufficient to apply two electrodes on the non-dominant hand of the experimental subject, on the index and middle fingers.
The GSR signal can be further decomposed into two components of interest: the tonic component and the phasic component.
Difference between tonic and phasic component in the galvanic skin response (GSR) [Neuromarketing]
The tonic component, also known as the skin conductance level (SCL), is a component subject to slow and gradual changes, in the order of seconds and minutes.
It is a component that is affected by certain skin characteristics such as dryness and hydration and can differ from person to person.
On the other hand, the phasic component, also known as the skin conductance response (SCR), is a faster and more suitable for studying the emotional state of people. In addition, some relevant metrics, such as the number of “GSR peaks“, are detected starting from the analysis of the phase component.
Why use GSR / EDA in Neuromarketing
In summary, why do Neuromarketing experts use sensors for the detection of the galvanic skin response (GSR)?
- Ease of integration with other techniques: the sensors for the detection of GSR can be easily inserted into an integrated system that involves the simultaneous use of different techniques such as Electroencephalography (EEG), Eye Tracking, Electrocardiography (ECG), Plethysmography (PPG) and Facial Coding.
- Intensity of Emotions: GSR analysis allows experts to measure people’s emotional involvement. For example, it is possible to identify which moments in a television advertisement generate the most intense emotions, or which banners on a website are most effective in terms of emotional involvement.
- Accessibility: today it is possible to purchase devices for measuring skin conductance at extremely low cost.
- Simplicity of measurement: the registration procedure is very fast and absolutely non-invasive.